The ‘Devils Staircase’ is a famous function in mathematics. It is a non-constant function that has $0$ derivative almost everywhere. Further it is continuous but not absolutely continuous.
Constructing the devils staircase is easy, and is done recursively. We start with the function $f_{0}:[0,1]\to[0,1]$ where $f_{0}(x)=x$. Now suppose we have defined $f_{n}$ we define $f_{n+1}$ by letting it be $1/2$ on the interval $[1/3,2/3]$, then we take a copy of the full function $f_{n}$ and “squash” it into the box with vertices : $(0,0),(1/3,0),(1/3,1/2),(0,1/2)$, then again we take a copy of $f_{n}$ and we “squash” it into the box with vertices $(2/3,1/2),(1,1/2),(1,1),(2/3,1)$, and that’s it we have defined $f_{n+1}$ on the interval $[0,1]$.
Taking the limit $n\to \infty$ we get the Cantor function
Here is an image of the construction:
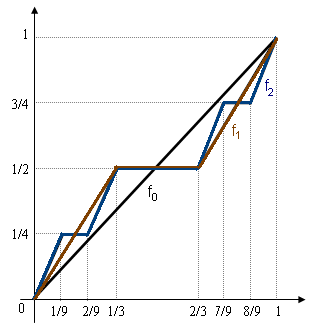
Great content for maths!
The way you break down concepts and provide real-life examples truly helps me grasp the material. Keep up the fantastic work
A good read indeed
Good findings
Interestingly woven
The step-by-step explanation of the Cantor function is helpful.
This is interesting